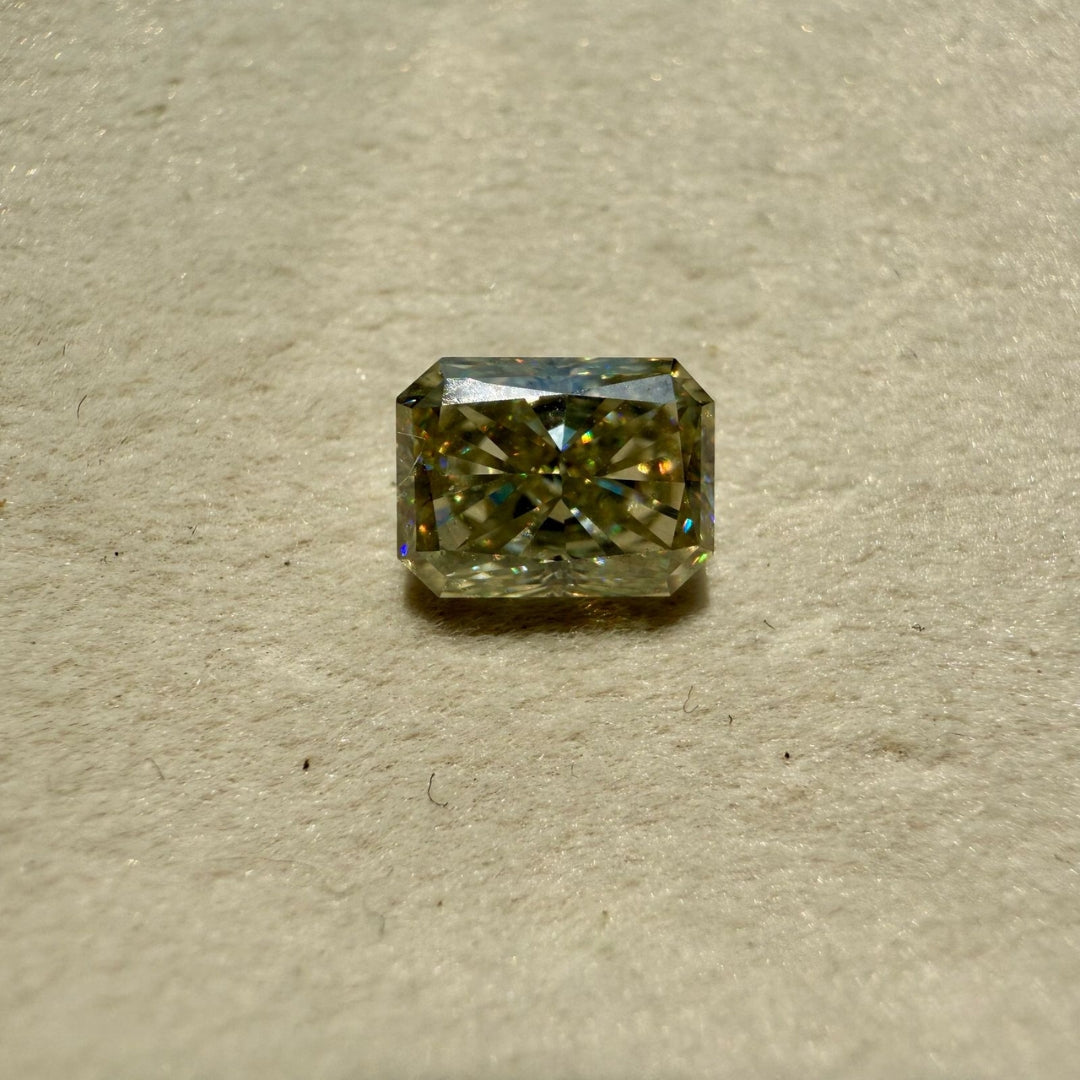
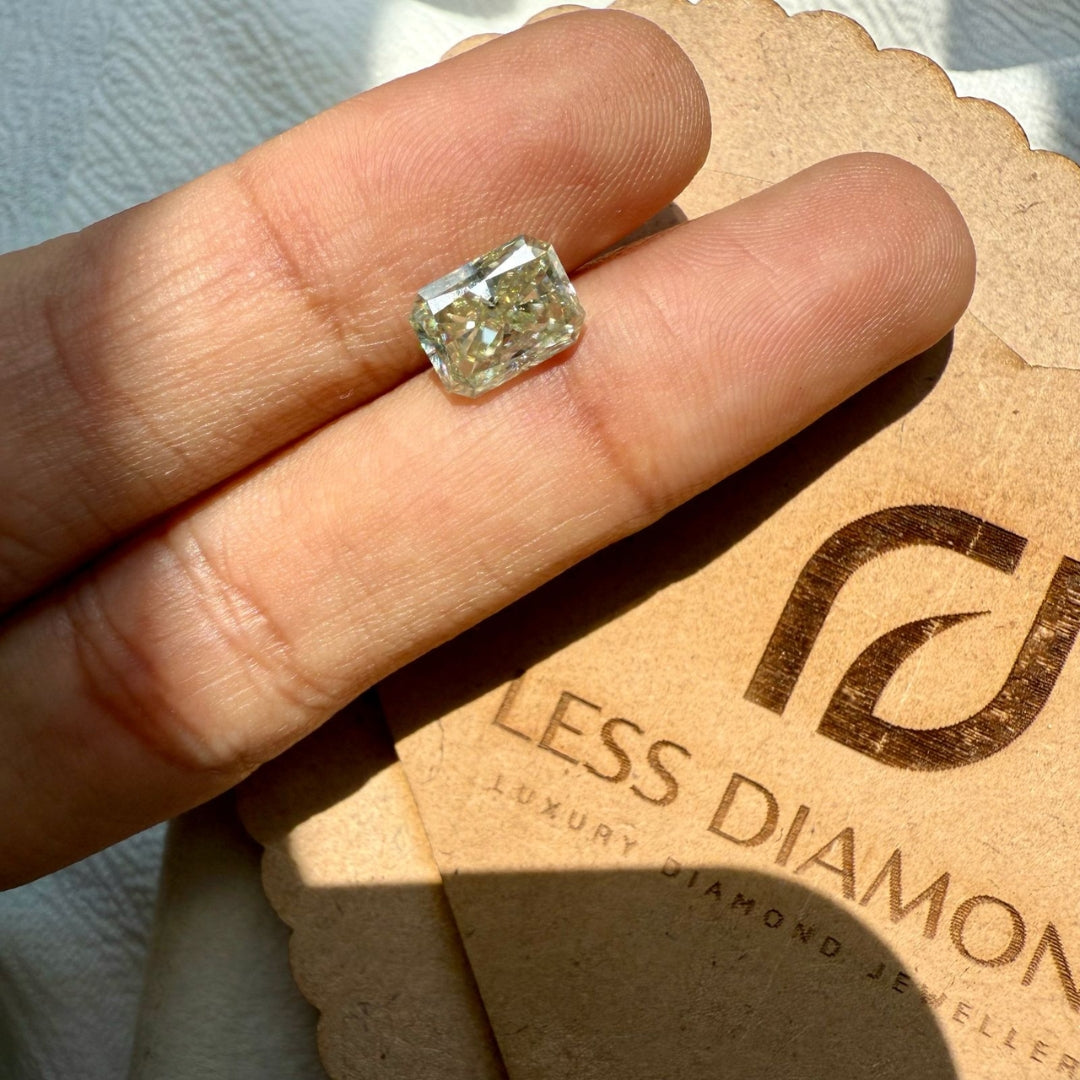
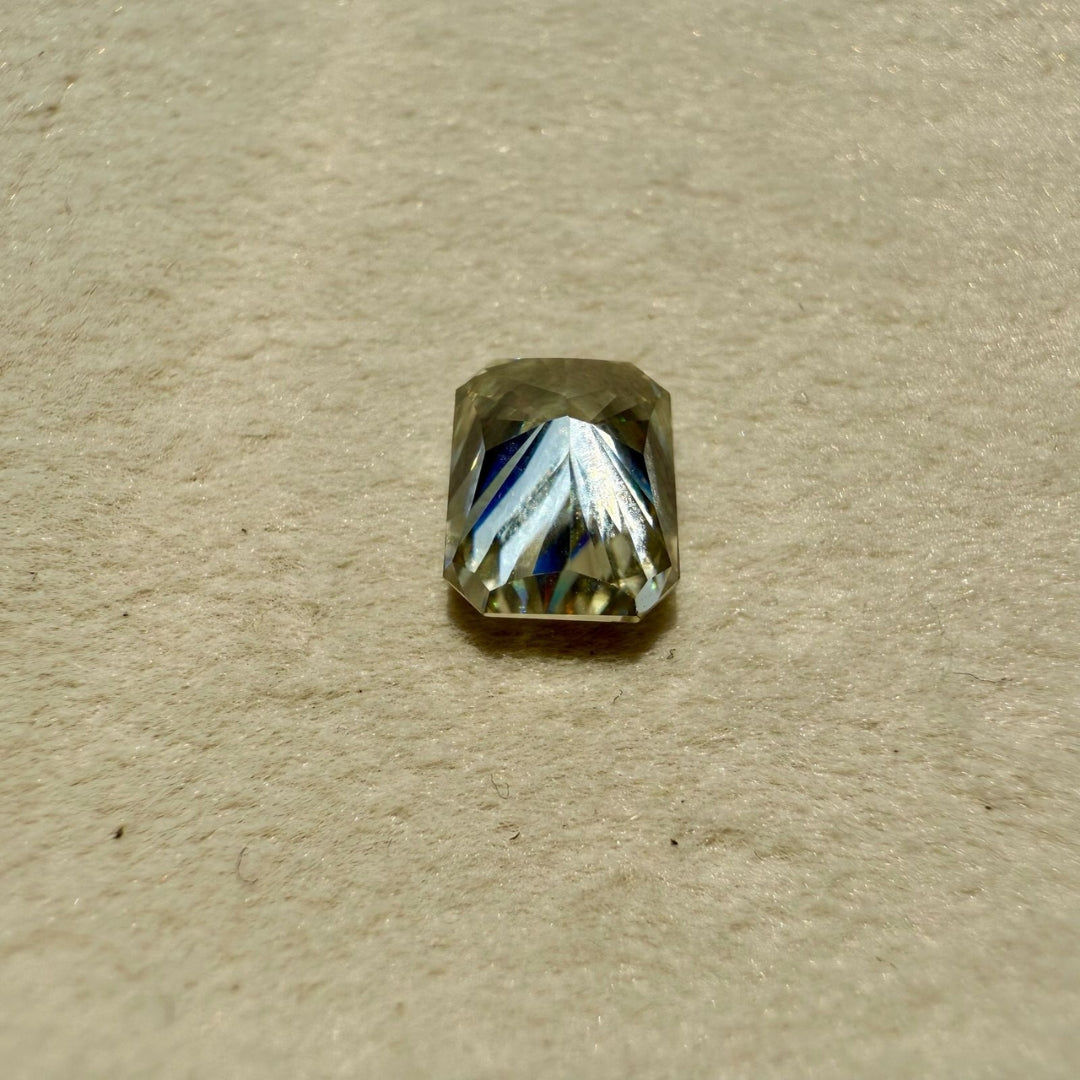
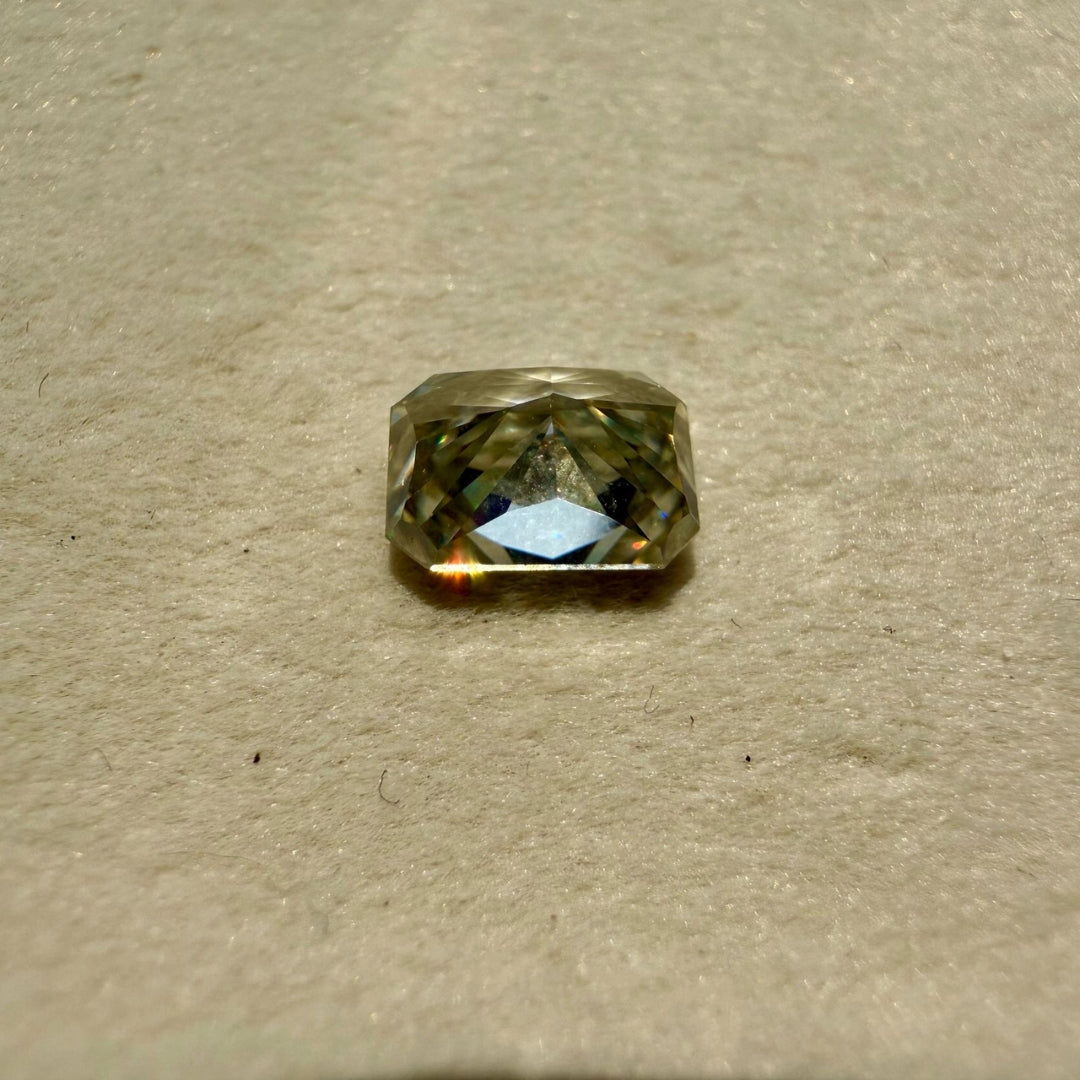
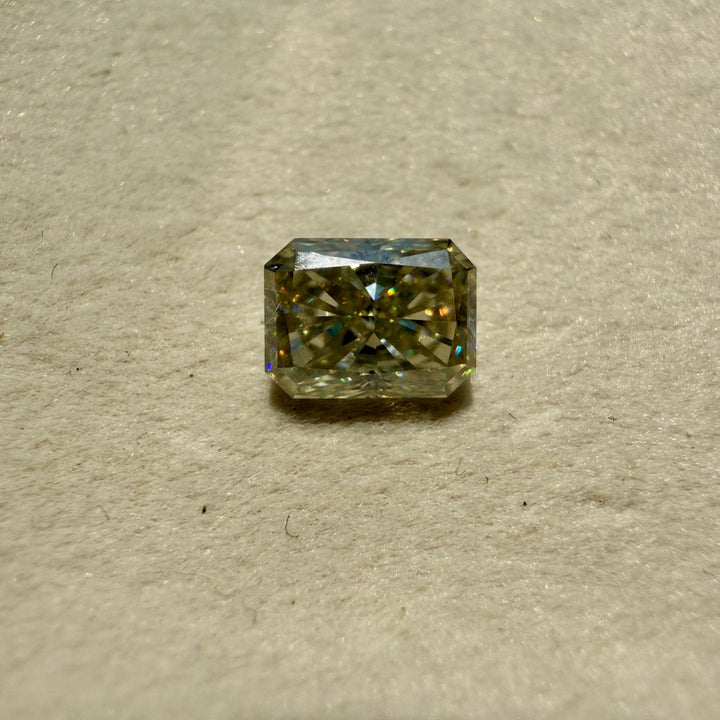
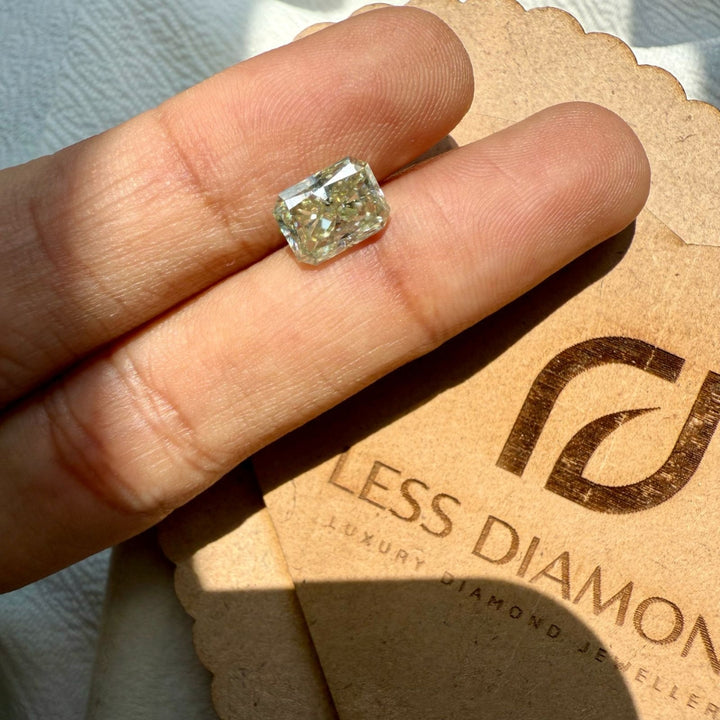
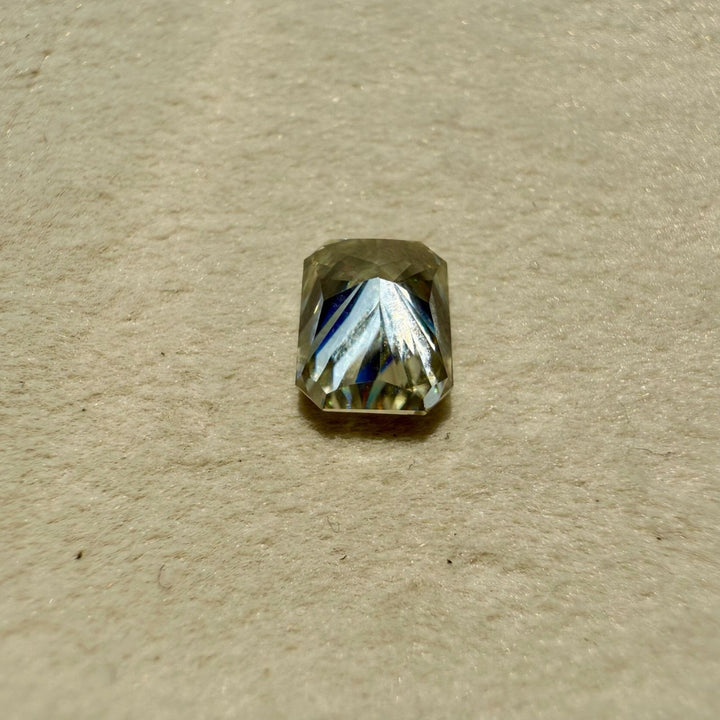
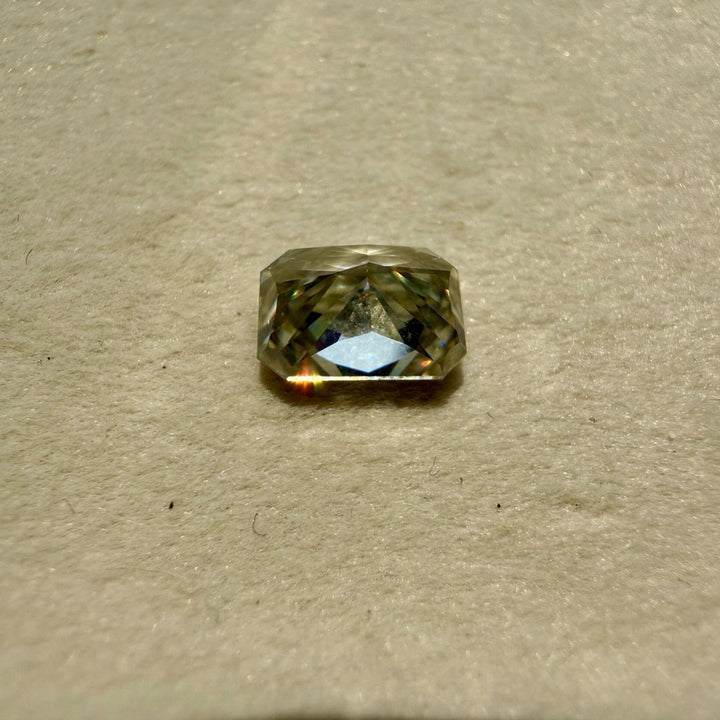
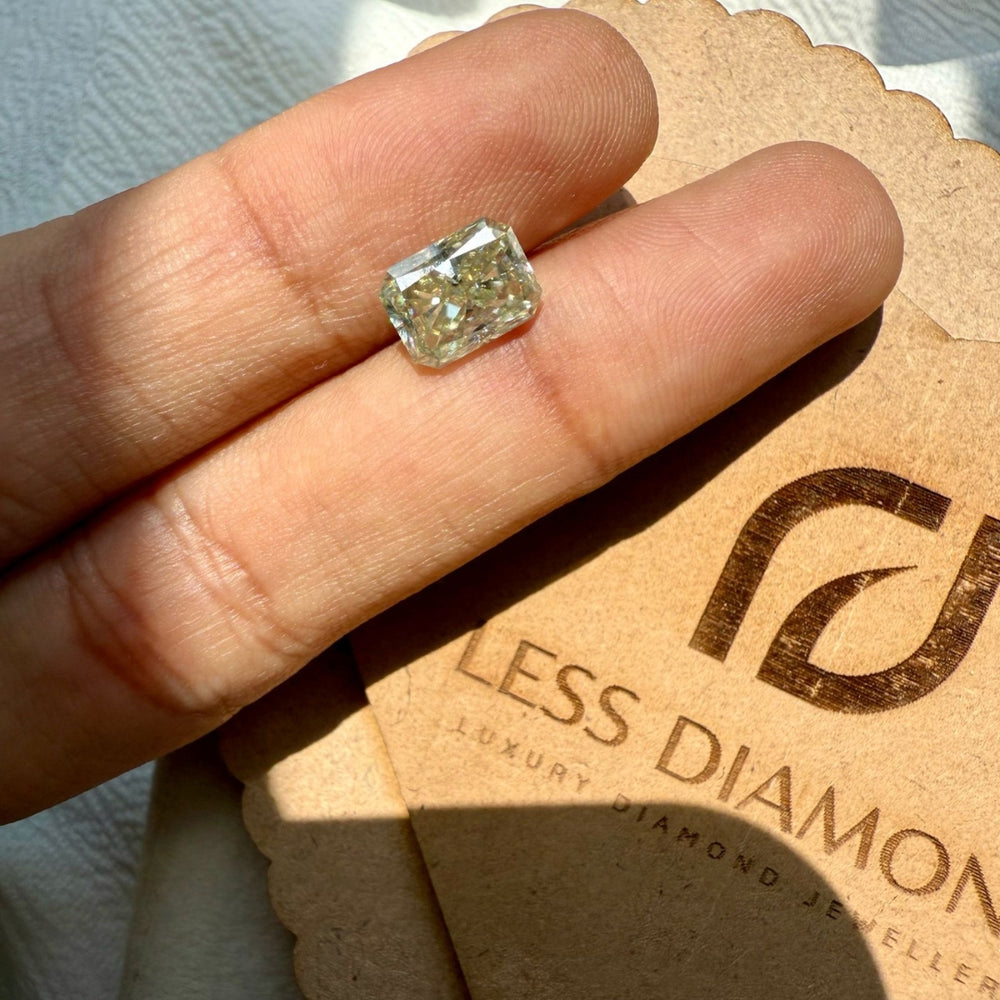
Moissanite 2.44 CT Radiant Loose Diamond
No reviews
- In stock, ready to ship
- Backordered, shipping soon
Ordered
»
Shipped
»
Delivered
Easy 14-day Return
100% Certified Diamonds
6-Month Warranty
Free Engraving
×
![Feature Icon]()
Title
Description goes here...

FLAT 15% Off on all Silver Jewelery

FLAT 25% Off on all 10KT Gold Jewelery

FLAT 35% Off on all 14KT Gold Jewelery

FLAT 45% Off on all 18KT Gold Jewelery
Description of Moissanite Loose Diamond.
Stone Details:
Stone : Moissanite
Shape : Radiant
Color : White
Size : 2.44 CT
- Customization Options : This Design Can Be Made With Gemstones Of Your Choosing. If You Would Prefer A Custom Ring, Please Contact Us Before Purchase.
- Material: Silver, White Gold, Yellow Gold, Rose Gold
- Ring Size: We Are Using US Metric System.
- You Can Send Us An Email Or Can Send A Message 24*7 For Any Service Required Thereafter.
- Please Select The Material And Ring Size From The Drop-Down Menu On The Right Side Of The Listing.
- If You Have Any Special Requests Or Questions, Please Do Not Hesitate To Contact Us.
- Free Insured Shipping: The Item Will Be Gift Wrapped And Shipped With Insured Express Shipping From.
- Custom Order Will Not Be Cancel.
- If You Want To Give The Return Your Pretty Ring To Us In Future, So We Will Take Return And Will Refund Your Amount Except PayPal Transaction Fees.
- Manufacturing Time Is Approx 3-5 Business Days.
- We Use UPS And Fedex As Our Shipping Partners For United States, Canada, United Kingdom, And Etc. Shipping Takes 4-6 Maximum Business Days To Deliver Your Parcel To Your Doorstep After We Ship Your Ring.
- Our 30-Day Money Back Guarantee Allows You The Time To Ensure Your Purchase Is Perfect.